Summary
- Turbochargers have revolutionized the automotive industry by allowing smaller, more fuel-efficient engines to achieve high performance, while also contributing to sustainability efforts and shaping the future of mobility.
- Turbochargers increase engine power and efficiency by forcing more air into the cylinders, resulting in more powerful combustion and improved fuel economy, making them environmentally friendly.
- Turbochargers have drawbacks including turbo lag, increased engine wear and tear, increased complexity, and higher cost compared to naturally aspirated engines.
The term “turbocharged” often conjures images of enhanced performance, and this association is well-founded. Originally developed for aircraft applications, turbo engines have now become commonplace in both gasoline and diesel-powered automobiles. Turbochargers are basically air compressors that increase the density of air taken in by the engine, a process which is known as forced induction. The other device used by car manufacturers to do this is the supercharger, which is a whole other topic in itself. Turbo engines have played a pivotal role in the significant performance advancements seen in cars over the years. However, what precisely constitutes a turbo engine in the automotive context, and how does it function?
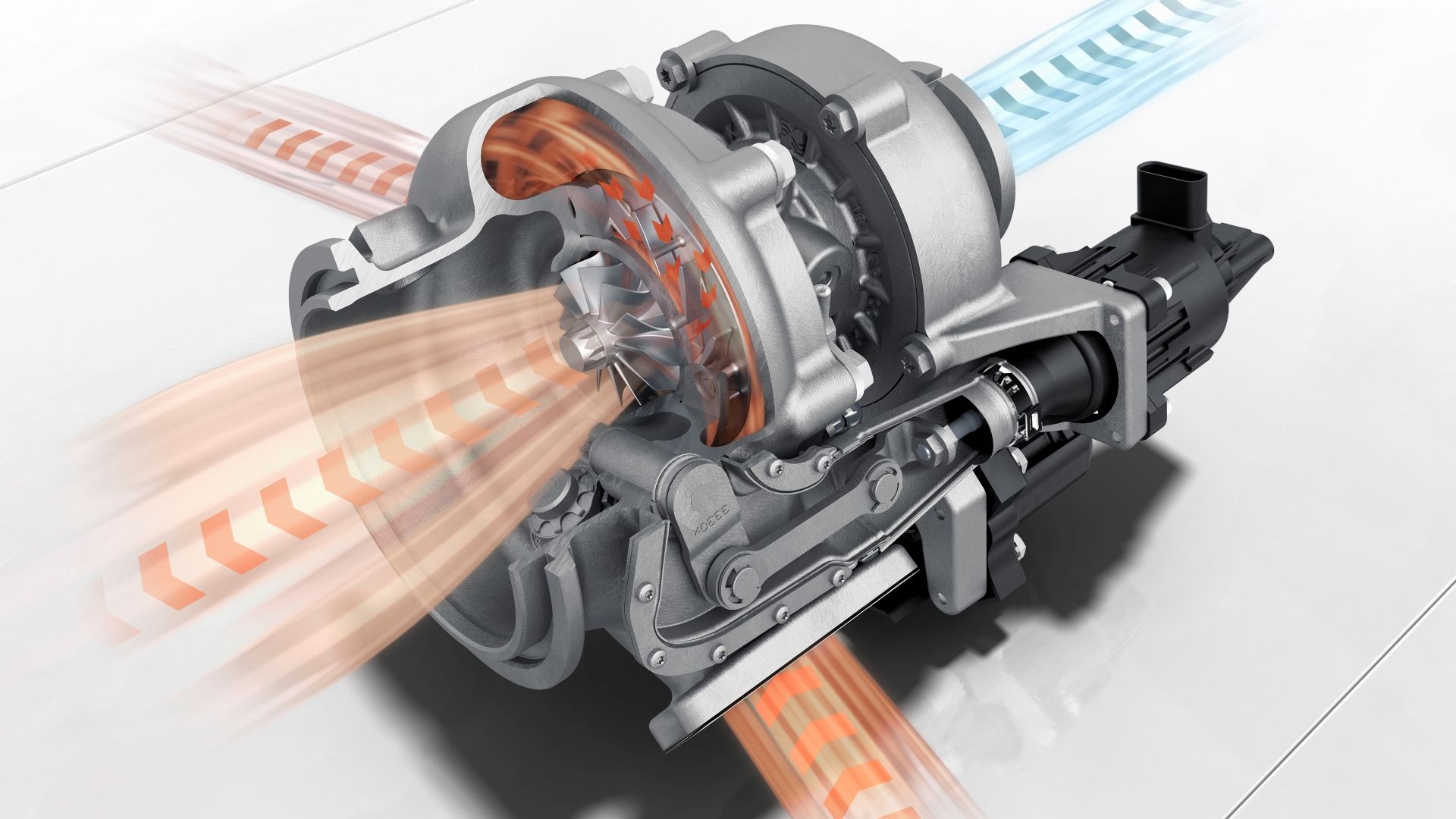
The turbocharger is composed of two main components: a turbine and a compressor. The turbine is located in the exhaust manifold of the engine. The flow of exhaust gases causes the turbine to spin. On the other end, the compressor is connected to the same shaft as the turbine, located on the intake side of the engine. As the turbine spins, it drives the compressor. The compressor’s primary function is to draw in and compress air from the surroundings before it enters the engine’s intake manifold. The key principle behind turbocharging is to force more air into the engine’s cylinders than it can naturally draw in on its own.
This increased air supply allows for a more significant amount of fuel to be burned, resulting in more powerful and efficient combustion. The benefits of turbocharging include increased engine power, improved fuel efficiency (when not in boost), and reduced emissions. Modern engines utilize sophisticated engine control units (ECUs) that monitor various parameters, including boost pressure, air-to-fuel ratio, and exhaust gas temperatures, to optimize engine performance and protect against over-boost conditions.
The Invention Of Turbochargers Forever Changed The Nature Of Engines
Turbochargers were designed to significantly enhance an engine’s performance by increasing power output and efficiency. Through improved combustion efficiency, they not only boost fuel economy but also contribute to a reduction in pollution, making them environmentally friendly. One of their remarkable attributes is their capacity to provide more power without the need for a larger engine, effectively being the replacement for displacement.
Moreover, turbochargers boast a relatively simple construction and operate autonomously, requiring no additional power from the engine or batteries, thus seamlessly integrating into the heart of the vehicle’s powertrain. These qualities make turbochargers an integral component of modern automotive engineering, delivering the perfect blend of power, efficiency, and environmental responsibility. However, for all of their advantages, they have their own set of drawbacks as well.
Drawbacks Of Turbocharging
- Turbo Lag
- Engine Wear And Tear
- Increased Complexity
- More Expensive
This is a common phenomenon faced by vehicles equipped with turbochargers. Turbochargers require time to spool up after the accelerator pedal is pressed to generate the necessary pressure within the combustion chamber to boost the engine. The presence of turbo lag can be attributed to variables like engine size and calibration, the efficiency of the turbine, and exhaust back pressure.
With turbo lag, engines face difficulty in executing seamless acceleration, making for a less-than-smooth driving experience. Car manufacturers have come up with some innovative ways to reduce turbo lag, for example, Audi was the first company to use an electric-powered turbocharger in their SQ7 SUV back in 2016.
This turbo was permanently spooled up to ensure almost zero lag. The additional stress placed on engine components due to increased pressure and heat can lead to accelerated wear and tear. Over time, this can manifest in issues such as worn-out engine components like piston rings, exhaust valves, and bearings.
It’s essential for vehicle owners to be aware of the potential for increased maintenance demands when driving a turbocharged car, including more frequent oil changes and vigilance in monitoring engine health to address issues promptly and prevent more extensive damage. Regular maintenance and following manufacturer-recommended service intervals are crucial to mitigate these concerns and ensure the long-term reliability of a turbocharged engine.
The incorporation of turbochargers necessitates the inclusion of supplementary components, including intercoolers, sensors, and the associated intricate plumbing systems, thereby complicating the production of the engine. Moreover, the implementation of turbochargers, especially in smaller engines, mandates the utilization of more robust internal components, meticulously engineered to withstand the heightened mechanical stress and elevated temperatures generated as a result of forced induction.
Turbocharged cars tend to come with a higher price tag compared to naturally aspirated (NA) cars due to several factors. Firstly, the addition of a turbocharger system itself involves extra manufacturing costs. These components are not only expensive to produce but, also require intricate engineering and precise calibration to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Moreover, turbocharged engines often demand the use of stronger and heat-resistant materials for internal components to withstand the increased stress and higher temperatures generated by forced induction. All of these factors contribute to the overall cost, making turbocharged cars a premium choice for those seeking enhanced power and performance.
Turbochargers: The Driving Force Behind Modern Engine Advancements
In conclusion, turbocharged engines have not only revolutionized the automotive industry but have also become an indispensable cornerstone of modern engine design. These remarkable components, born from the aviation world, have seamlessly transitioned into the realm of automobiles, bringing with them a plethora of advantages that have redefined what we expect from our vehicles.
Turbochargers enable our cars to accelerate with astonishing speed, conquer steep climbs, and most importantly provide a fun driving experience that was once the realm of sports cars. The ability to extract more power from a smaller engine has also paved the way for downsized, more fuel-efficient power plants, contributing to improved fuel economy.
Turbochargers Continue To Change With The Times
Furthermore, turbochargers have played an instrumental role in the ongoing quest for cleaner and more environmentally responsible transportation. By optimizing combustion efficiency, they help reduce the production of harmful pollutants. In essence, turbocharging has become a critical tool in the automotive industry’s commitment to sustainability, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
In today’s automotive landscape of the dying ICE engine, where stringent emissions regulations and fuel economy standards reign supreme, turbochargers are the unsung heroes. They allow automakers to strike a delicate balance between power and efficiency, offering drivers the best of both worlds. Turbocharging technology continues to evolve, with innovative solutions such as e-turbos and twin-scroll designs, further enhancing performance while mitigating traditional challenges.
The advent of turbochargers has disrupted the age-old belief that larger engines are the only path to increased performance. Turbocharged engines have ushered in an era where compact, lightweight powerplants can outperform their larger, naturally aspirated counterparts. This shift has far-reaching implications, especially in upcoming hybrid engines which are being reduced in size to account for their electric components.
Turbochargers have always propelled the automotive industry forward, forcing engineers and manufacturers to think differently and embrace the potential of smaller, more efficient engines. They have not only met the demands of enthusiasts seeking exhilarating speed but have also met the needs of a planet in search of cleaner transportation options.
As we stand at the precipice of a new era in transportation, turbocharged engines remain at the forefront of innovation and progress. Their enduring importance cannot be overstated, as they continue to shape the vehicles we drive, the fuels we use, and the future of mobility itself. Turbochargers, once the purview of high-performance cars, are now a fundamental pillar of the modern engine, driving us toward a more sustainable, efficient, and exciting automotive future.